The global community is focused on novel ways to solve issues in an era marked by a growing commitment to decarbonization and increased scrutiny of corporations’ Environmental, Social, and Corporate governance (ESG) standards. The increasing demand for hydrogen as a crucial player in decreasing greenhouse gas emissions and reaching ambitious sustainability targets is at the forefront of this disruptive wave.
Hydrogen Adoption Driving Forces:
Decarbonization and ESG Priorities:
Customers and investors both recognize the urgency of combating climate change. Companies are becoming increasingly evaluated based on their progress toward environmental sustainability goals. Hydrogen, primarily derived from renewable sources, emerges as a potent alternative for lowering carbon footprints and promoting sustainable energy.

Water-related Challenges:
While water is required for hydrogen production, there is a significant difference between the water quality needed for electrolysis and the norms for safe drinking water. The purification process is expensive, necessitating additional research and development to increase equipment efficiency and decrease dependency on ultra-pure water. Advances in fuel cell regeneration technologies provide a ray of hope that demands more exploration.
Applications of Hydrogen:
The versatility of hydrogen is shown in its wide applications, ranging from internal combustion engines and fuel cells to blending with natural gas in existing infrastructure. Integrating hydrogen into the national gas grid lowers the carbon intensity of existing systems while reducing the demand for specialized hydrogen distribution and storage networks.
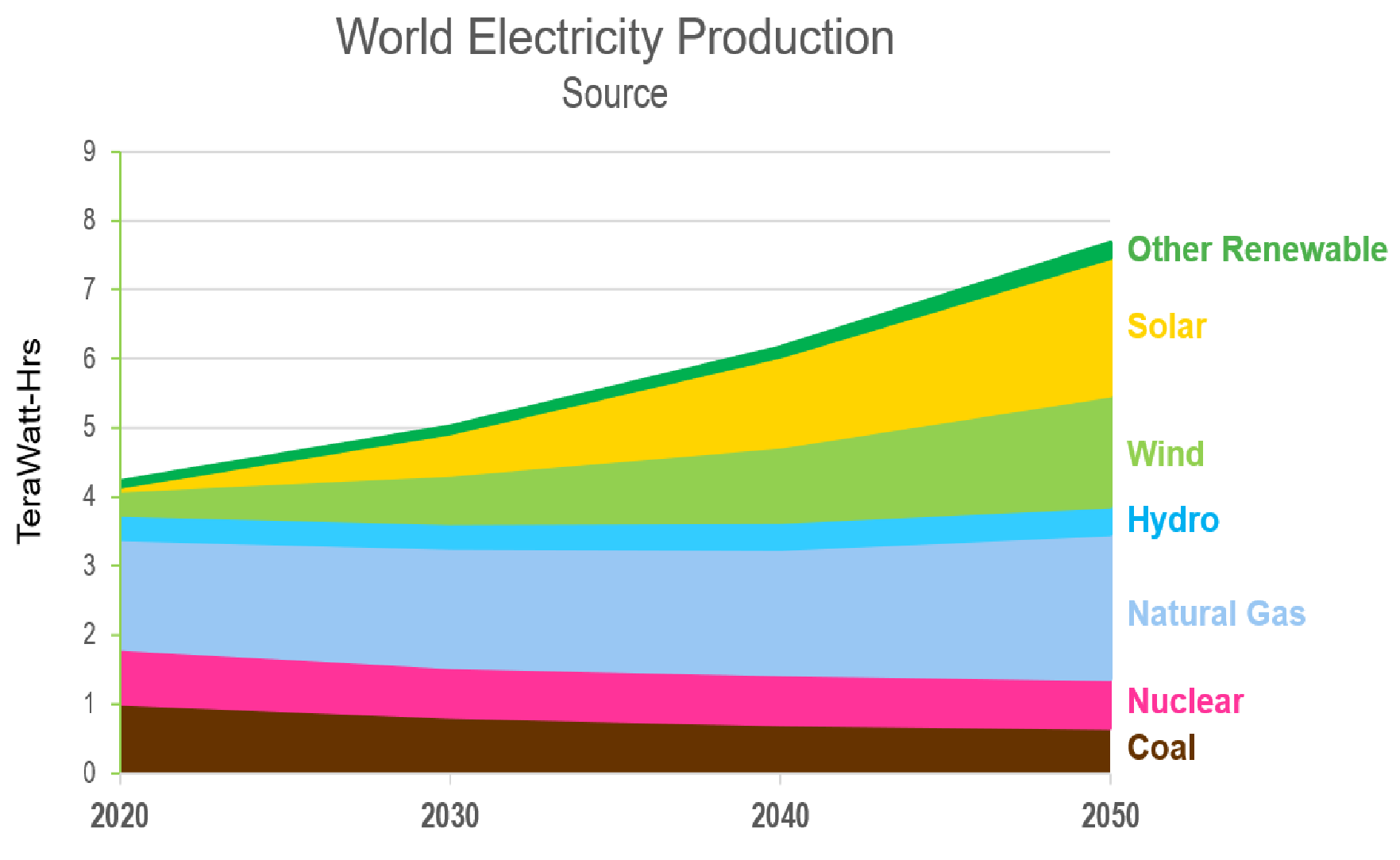
Renewable Energy Generation and Storage Challenges:
The rise of variable renewables such as wind and solar electricity brings a new challenge, i.e. Storage. Hydrogen is a promising answer since it can store renewable energy at Domestic and Global levels. This balances the demand-supply imbalance while also promoting a more sustainable energy infrastructure.
Hydrogen Safety Solutions:
Because hydrogen is odorless and almost invisible in the daylight, it poses safety concerns. On the other hand, wearable sensor developments and stringent safety measures overcome these concerns. To ensure the safe integration of hydrogen technologies, hazards connected with combustion, explosion, and cryogenic liquid handling must be mitigated consistently.

Key Takeaways and Challenges:
- Net zero emissions:
Governments worldwide have committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2070, highlighting the necessity of carbon capture and hydrogen generation solutions. The public sector must link policies with successful technological players to speed the shift to sustainable practices.
- Bridging Traditional and Sustainable Technologies:
A harmonic blend of traditional and alternative technologies can be seen as the shift progresses. Adapting to changing market trends while remaining committed to sustainability is critical. This synergy will allow for a more seamless and effective integration of hydrogen into existing energy systems.
- Attaining the Full Potential:
Understanding the entire value chain is essential. This includes assessing the financial implications of hydrogen generation, water usage, effective renewable energy utilization, and hydrogen safety. By overcoming these issues, the industry will realize the full potential of hydrogen as a sustainable energy alternative.
To summarize, hydrogen is critical in transitioning to a more sustainable future. To overcome hurdles and fully realize the potential of hydrogen as a clean energy source, the global society must participate in extensive deliberation. We can pave the path for a greener and more sustainable tomorrow by taking a comprehensive strategy that includes technology, legislation, and safety issues.
Green Power International is dedicated to negotiating the challenges of the energy transition and advocating for solutions that contribute to a cleaner and sustainable future. Join us on this profound exploration of a hydrogen-powered future.